Reflections with HDRI
In this lesson we are going to learn how to do reflections inside 3DS Max using HDR Images and Panoramas. In order to learn how to capture a basic ‘Panorama’ and ‘HDR image’ you guys can have a look at the articles on ‘HDR Image’ and ‘Panoramas’ covering all the basic steps involved in the process.
01 Now we will further improvise the IBL scene by adding in some metallic objects into it. Open up the ‘Slate Material Editor’ by pressing ‘M’ on the keyboard and create a ‘Raytrace’ material inside it from the right click menu.
02 Add in the HDR Panorama Image of the scene inside the ‘Environment’ slot of the ‘Raytrace’ Material. Bring up the ‘Specular Level’ to ’90’ and ‘Glossiness’ to ‘100’ in order to get a super glossy metallic finish out of the material. Also change the diffuse color to a darker shade of red.
03 Change the ‘Reflect’ Method to ‘Fresnel’ by clicking onto the Reflect Text in order to toggle between the different reflection methods. Bring up the value of ‘Index of Refraction’ to ‘1.7’ in order to make the material more reflective.
04 Create a Sphere object in the scene and apply this Raytrace Material onto it in order to see the result in the render. Fresnel reflections has helped us in altering the reflectivity of the material so that it becomes much more reflective on the edges. The Material becomes much more reflective as the angle of the surface moves away from perpendicular to the viewer as we can notice on the top right side and bottom edges.
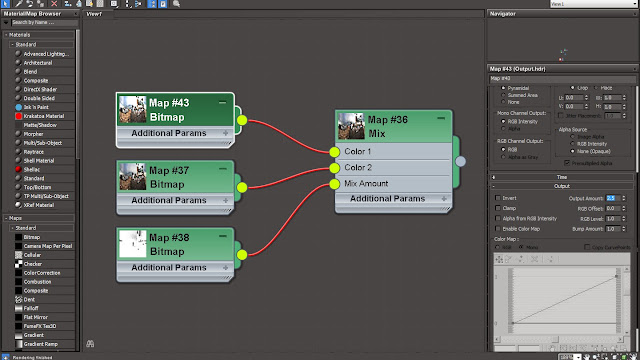
05 Now we will improvise the result by improvising the effect of the current HDR Image. We will achieve it by creating a Mix Map inside 3DS Max and blending up the standard HDR and a boosted HDR from Photo-shop. Bring in a ‘Mix’ map inside the ‘Material Slate Editor’ from the right click menu.
06 Open the HDR Image of the scene inside Photo-shop and convert it into a ‘Gray-scale’ Image from the ‘Mode’ options inside the ‘Image’ menu. We will further modify the gray-scale values of the image with the help of ‘Levels’ settings accessible from the ‘Adjustment’ options inside the ‘Image’ menu.
07 We will tweak the ‘Levels’ settings in order to change all the light areas on the image into bright white and the darker areas into more dark or black. But while tweaking it we have to make sure that the gray-scale balance effects the white hotspots on the image.
08 In order to save this modified version into a JPEG file we have to tone it down from 32bits/channel to 8bits/channel version from the ‘Mode’ options available inside the ‘Image’ menu. From the ‘HDR Toning’ dialogue box select the ‘Exposure and Gamma’ method for reducing the bits/channel amount. Save the file while renaming it as ‘Output_Grayscale.jpg’.
09 Bring up the ‘Mix’ Map Parameters and load the ‘Output.hdr’ file inside the ‘Color #1’ and ‘Color #2’ map slots and load the ‘Output_Gray-Scale.jpg’ file inside ‘Mix Amount’ map slot. Dive inside each of the Maps Parameters and decrease the ‘Blur’ amount to ‘0.01’.
10 Inside the ‘Output’ options of ‘Output_Gray-Scale.jpg’ loaded inside the ‘Mix Amount’ map slots turn on the ‘Invert’ option in order to invert the gray-scale effect on the blending. This option will reverse the effect of mask so that we can modify the areas that are white in our mask, and use the normal bitmap in all other areas.
11 Bring up the value of the ‘Output Amount’ from ‘Color #1’ map ‘Output’ parameters to ‘2.5’. This will help in boosting up the color levels of the map giving a good quality HDR Image based result.
12 Now we will replace the ‘HDR Panorama Image’ linked to the ‘Environment’ map slot of our Raytrace Material with the new ‘Mix Map’. Hit render in order to see the result achieved by us so far.